What is Blockchain? How It Works and Real-World Applications

Discover what blockchain is, how it works, and its real-world applications. Learn about the technology behind cryptocurrencies and its transformative potential.
What is Blockchain? How It Works and Real-World Applications
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we think about data security, transparency, and decentralization. Originally developed as the underlying technology for Bitcoin, blockchain has since found applications in various industries. In this article, we’ll explore what blockchain is, how it works, and its real-world applications.
What is Blockchain?
A blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. Each block in the chain contains a list of transactions, and once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered. This ensures transparency, security, and immutability.
- Key Features:
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the blockchain.
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to network participants.
- Immutability: Once recorded, data cannot be changed or deleted.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Understanding how blockchain works involves breaking down its core components and processes:
1. Blocks
Each block contains a list of transactions, a timestamp, and a reference to the previous block (hash).
2. Chain
Blocks are linked together in a chronological order, forming a chain.
3. Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms ensure that all participants agree on the state of the blockchain.
- Common Mechanisms:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Miners solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake.”
4. Nodes
Nodes are computers that participate in the blockchain network, maintaining a copy of the entire blockchain and validating transactions.
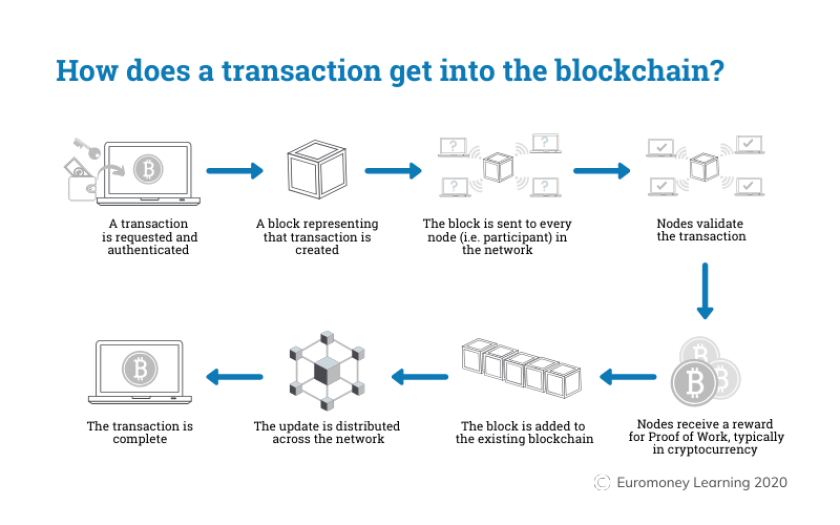
Real-World Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has a wide range of applications beyond cryptocurrencies. Here are some notable examples:
1. Financial Services
Blockchain is transforming the financial industry by enabling faster, cheaper, and more secure transactions.
- Use Cases:
- Cross-border payments.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi).
- Smart contracts for automated financial agreements.
2. Supply Chain Management
Blockchain enhances transparency and traceability in supply chains.
- Use Cases:
- Tracking the origin and journey of products.
- Reducing fraud and counterfeiting.
- Improving inventory management.
3. Healthcare
Blockchain is improving data security and interoperability in healthcare.
- Use Cases:
- Secure sharing of medical records.
- Tracking pharmaceuticals and medical devices.
- Managing patient consent and data access.
4. Voting Systems
Blockchain can enhance the security and transparency of voting systems.
- Use Cases:
- Preventing voter fraud.
- Ensuring the integrity of election results.
- Enabling remote and secure voting.
5. Intellectual Property
Blockchain is being used to protect intellectual property rights.
- Use Cases:
- Registering and verifying ownership of digital assets.
- Managing royalties and licensing agreements.
- Preventing piracy and unauthorized use.
6. Real Estate
Blockchain is streamlining real estate transactions and reducing fraud.
- Use Cases:
- Simplifying property transfers.
- Reducing the need for intermediaries.
- Enhancing transparency in property records.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain offers several benefits that make it a transformative technology:
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to network participants, enhancing trust.
- Security: Cryptographic techniques ensure data integrity and security.
- Decentralization: Eliminates the need for a central authority, reducing the risk of single points of failure.
- Efficiency: Automates and streamlines processes, reducing costs and time.
- Immutability: Once recorded, data cannot be altered, ensuring a reliable audit trail.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its potential, blockchain technology faces several challenges:
- Scalability: Handling a large number of transactions can be challenging.
- Regulation: The regulatory environment is still evolving, creating uncertainty.
- Energy Consumption: Proof of Work (PoW) mechanisms consume significant energy.
- Adoption: Widespread adoption requires overcoming technical and educational barriers.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a groundbreaking innovation with the potential to transform various industries. By providing transparency, security, and decentralization, blockchain offers a new way to manage and secure data. Whether you’re interested in finance, healthcare, supply chain, or beyond, understanding blockchain is essential for navigating the future of technology.
Call to Action: Ready to explore the world of blockchain? Start by learning more about its applications and potential. Join the blockchain community and take the first step toward understanding this transformative technology!